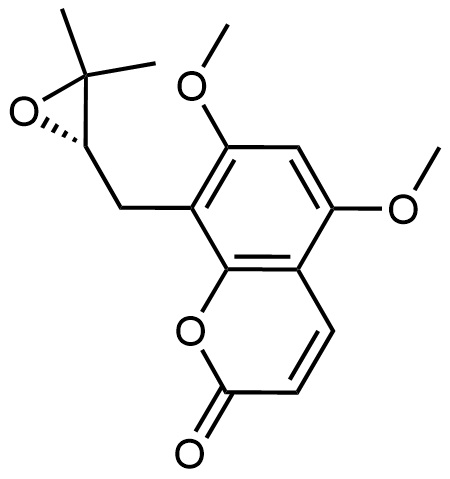
| 英文名稱 | Sibiricin |
|---|---|
| 中文名稱 | Sibiricin | (S)-8-[(3,3-二甲基環(huán)氧乙烷基)甲基]-5,7-二甲氧基-2H-1-苯并吡喃-2-酮 |
| CAS號 | 95188-34-4 |
| 分子式 | C16H18O5 |
| 分子量 | 290.31 |
| 儲存條件 | Store in a dry and dark sealed container, short-term (weeks to months) storage at 0-4 ℃, long-term (months to years) storage at -20 ℃. |
- 021-58180488
- sales@MedChemLeader.com
-
抑制劑信號通路研究Autophagy | 自噬 Angiogenesis Apoptosis | 細胞凋亡 Cell Cycle | 細胞周期 Cytoskeletal Signaling | 細胞骨架 DNA Damage/DNA Repair Endocrinology & Hormones Epigenetics | 表觀遺傳學 GPCR & G Protein Immunology & Inflammation MAPK/ERK Pathway Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel Metabolism Microbiology/Virology/ Anti-infection Neuronal Signaling | 神經(jīng)信號通路 NF-κB PI3K/Akt/mTOR Proteases Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK Stem Cells & Wnt | 干細胞及 Wnt 通路 TGF-beta/Smad | 信號通路 Vitamin D Related Antibody-drug Conjugate/ADC Related PROTAC JAK/STAT 信號通路 Ox Stress Reagents(OX應激試劑)
-
凱立德生物商城首頁
-
10000+產(chǎn)品中心
- 信號通路>
- Autophagy | 自噬
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis | 細胞凋亡
- Cell Cycle | 細胞周期
- Cytoskeletal Signaling | 細胞骨架
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Endocrinology & Hormones
- Epigenetics | 表觀遺傳學
- GPCR & G Protein
- Immunology & Inflammation
- MAPK/ERK Pathway
- Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel
- Metabolism
- Microbiology/Virology/ Anti-infection
- Neuronal Signaling | 神經(jīng)信號通路
- NF-κB
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Proteases
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK
- Stem Cells & Wnt | 干細胞及 Wnt 通路
- TGF-beta/Smad | 信號通路
- Vitamin D Related
- Antibody-drug Conjugate/ADC Related
- PROTAC
- JAK/STAT 信號通路
- Ox Stress Reagents(OX應激試劑)
- 生命科學>
- 分子生物學
- 醫(yī)藥開發(fā)&藥物發(fā)現(xiàn)研究
- 細胞生物學
- 生物化學及試劑
- 糖科學|糖類化合物
- 雜質(zhì)與代謝物
- 氨基酸及其衍生物
- 多肽與蛋白
- Enzyme(酶)
-
精美商品積分商城
-
技術服務
-
關于我們
-
聯(lián)系我們
-
新聞中心